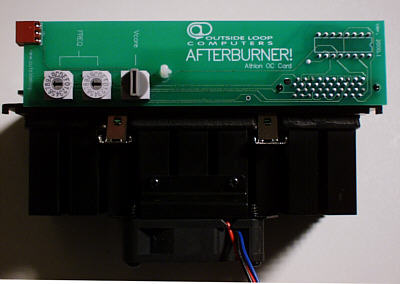
Introduction:
Computer processors can be overclocked by changing two different
settings. One of these is the "bus frequency" which runs at
66MHz for Celeron processors, and 100MHz for Pentium III processors
(neglecting 133MHz for now). Going above these values for either
processor is called "bus overclocking".
The second setting that can theoretically be changed to affect
processor speed is called the "multiplier". All processors
run faster than the bus frequency, because they can perform multiple
operations per clock cycle. So a 500MHz Pentium III is rated as such
because it has a 5X multiplier on a 100MHz bus. Changing a multiplier
setting to a higher value than set by the manufacturer is called
"multiplier overclocking".
Processor manufacturers have been putting so-called
"multiplier locks" on all of their processors for several years
now, which prevent using any multiplier other than the factory default.
This was not done so much to prevent overclocking, as it was to prevent illegal
"remarking" of chips.
Intel instituted multiplier locks on their Pentium II line of
chips in 1998. Since that time, you could only overclock newer Intel
processors by pairing them with a motherboard which allowed the user to
adjust the frequency of the bus clock generator. Intel's Pentium III
processors are renowned for their conservative rating, and ability to be
overclocked by upping the bus frequency. The Pentium III 450 often
could be run at a bus setting of between 124MHz and 130MHz, yielding total
speed ratings of between 558MHz and 585MHz.
Bus frequency overclocking has two consequences not found with
multiplier overclocking. These are the fact that bus overclocking
increases the speed of all the different parts of the motherboard, thus
speeding up all the other components in your computer. This is good
for improving performance, but it leads to the second consequence.
At some point, as you continue to increase the bus speed, either your
memory, video card, or one of your PCI cards is not going to be able to
handle the speed increase, and the computer will hang.
NEXT
=> The Afterburner
|